Table Of Content
Although remarkable advancements have been achieved in generative models, very few efforts have been paid to design relevant quality assessment models. In this paper, we propose a novel blind image quality assessment (IQA) network, named AMFF-Net, for AGIs. AMFF-Net evaluates AGI quality from three dimensions, i.e., "visual quality", "authenticity", and "consistency". After that, an Adaptive Feature Fusion (AFF) block is used to adaptively fuse the multi-scale features with learnable weights.
Model
When we can utilize these ideal designs, which have nice simple structure, the analysis is still very simple, and the designs are quite efficient in terms of power and reducing the error variation. To do a crossover design, each subject receives each treatment at one time in some order. So, one of its benefits is that you can use each subject as its own control, either as a paired experiment or as a randomized block experiment, the subject serves as a block factor.
The ANOVA for Randomized Complete Block Design (RCBD)
The simplest case is where you only have 2 treatments and you want to give each subject both treatments. Here as with all crossover designs we have to worry about carryover effects. In this factory you have four machines and four operators to conduct your experiment. Use the animation below to see how this example of a typical treatment schedule pans out. When the data are complete this analysis from GLM is correct and equivalent to the results from the two-way command in Minitab.
Procedure for Randomization
Table 2 : Efficiency of RBD in comparison to CRD when plots were... - ResearchGate
Table 2 : Efficiency of RBD in comparison to CRD when plots were....
Posted: Fri, 08 Jun 2018 16:57:07 GMT [source]
It is important to have all sequences represented when doing clinical trials with drugs. There are 23 degrees of freedom total here so this is based on the full set of 24 observations. Why is it important to make sure that the number of soccer players running on turf fields and grass fields is similar across different treatment groups? They have four different dosages they want to try and enough experimental wafers from the same lot to run three wafers at each of the dosages. Identify potential factors that are not the primary focus of the study but could introduce variability. This website is using a security service to protect itself from online attacks.
He pointed out that it would be unusual to use blocks in design of experiments as a way to check for the need for further experimentation. The reason is that, so far, I’ve been considering only variables that we can measure and manipulate. As the name implies, random experimental design involves randomly assigning experimental conditions.
Crossover Design Balanced for Carryover Effects
There should be few interactions between variables and very few variables that contribute significantly. Random design does not work very well with relatively smaller systems. Generally speaking, Taguchi and random designs often perform better than factorial designs depending on size and assumptions. When choosing the design for an experiment, it is important to determine an efficient design that helps optimize the process and determines factors that influence variability.
This gives us a design where we have each of the treatments and in each row and in each column. If this point is missing we can substitute x, calculate the sum of squares residuals, and solve for x which minimizes the error and gives us a point based on all the other data and the two-way model. We sometimes call this an imputed point, where you use the least squares approach to estimate this missing data point. The partitioning of the variation of the sum of squares and the corresponding partitioning of the degrees of freedom provides the basis for our orthogonal analysis of variance. In studies involving human subjects, we often use gender and age classes as the blocking factors. We could simply divide our subjects into age classes, however this does not consider gender.
Error
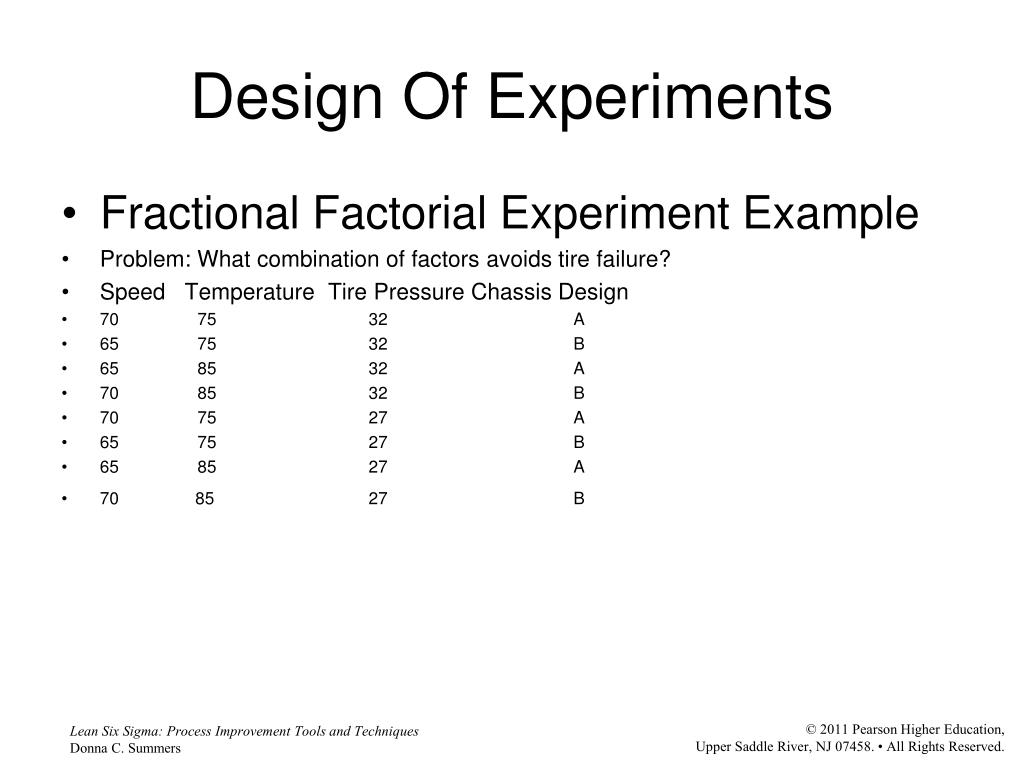
Let’s start with the basic 22 factorial design to introduce the effective use of blocking into the 2k design (Table 1). Let’s assume that we need at least three replications for this particular experiment. If one batch can produce enough raw materials for only four samples (experimental units), only one replication can be made from one batch. Therefore, three batches will be required to complete the three full replications for the 22 basic factorial design (Table 2). Random designs typically work well for large systems with many variables, 50 or more.
This carryover would hurt the second treatment if the washout period isn't long enough. The measurement at this point is a direct reflection of treatment B but may also have some influence from the previous treatment, treatment A. This is a Case 2 where the column factor, the cows are nested within the square, but the row factor, period, is the same across squares. If we only have two treatments, we will want to balance the experiment so that half the subjects get treatment A first, and the other half get treatment B first. For example, if we had 10 subjects we might have half of them get treatment A and the other half get treatment B in the first period. After we assign the first treatment, A or B, and make our observation, we then assign our second treatment.
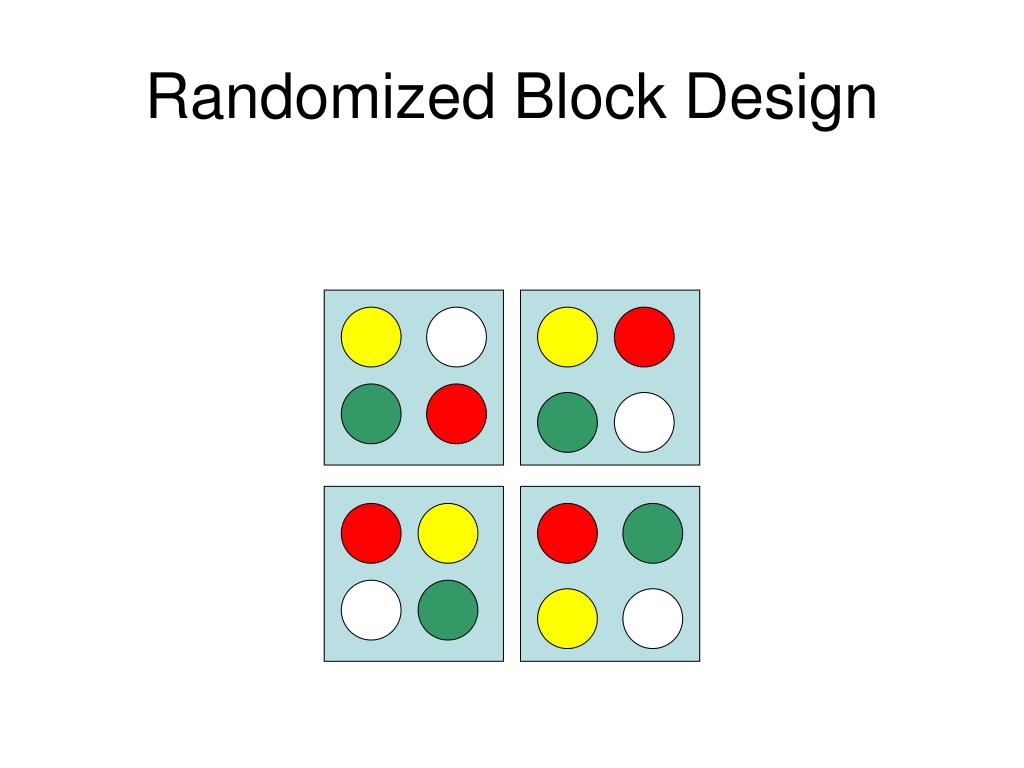
The use of blocking in experimental design has an evolving history that spans multiple disciplines. The foundational concepts of blocking date back to the early 20th century with statisticians like Ronald A. Fisher. His work in developing analysis of variance (ANOVA) set the groundwork for grouping experimental units to control for extraneous variables. There is more than one type of random design, randomized block design and completely randomized design. Randomized block design involves blocking, which is arranging experimental units into groups so they have a common similarity.
But eventually, there has to be some decline in catapult performance. I’ll plan to change the catapult each time I collect a complete set of data for the experiment. That way, I’m only using a catapult for a number of launches that I think won’t cause fatigue. Completely randomized design (CRD) is the simplest type of design to use. The most important requirement for use of this design is homogeneity of experimental units.

No comments:
Post a Comment